Laparoscopic Tuboplasty in Pune
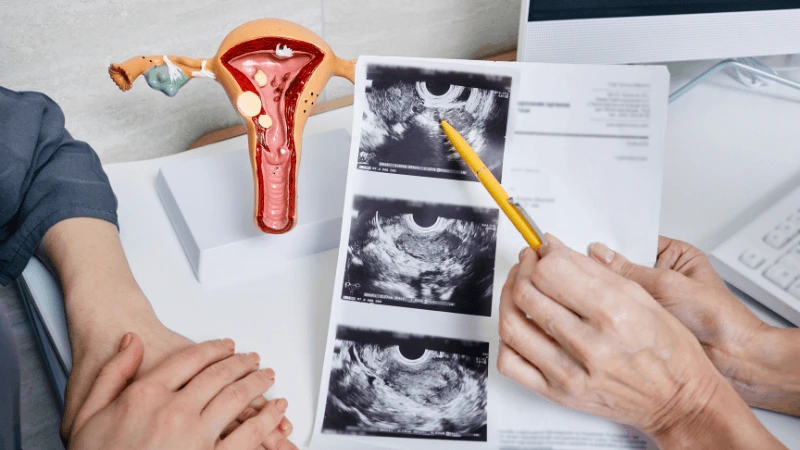
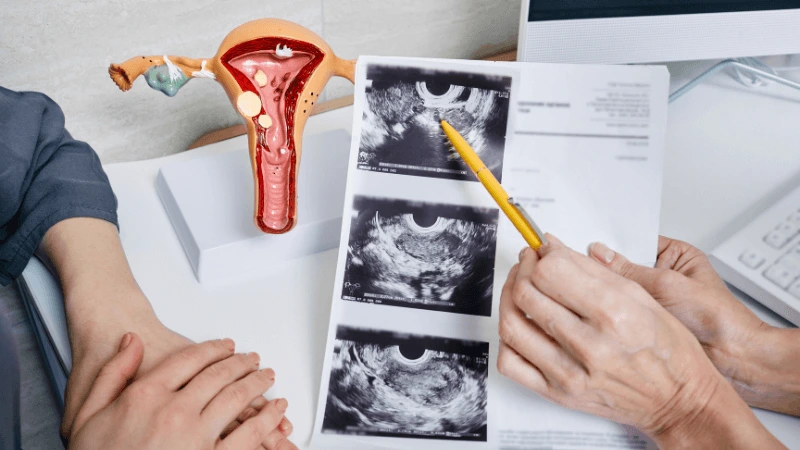
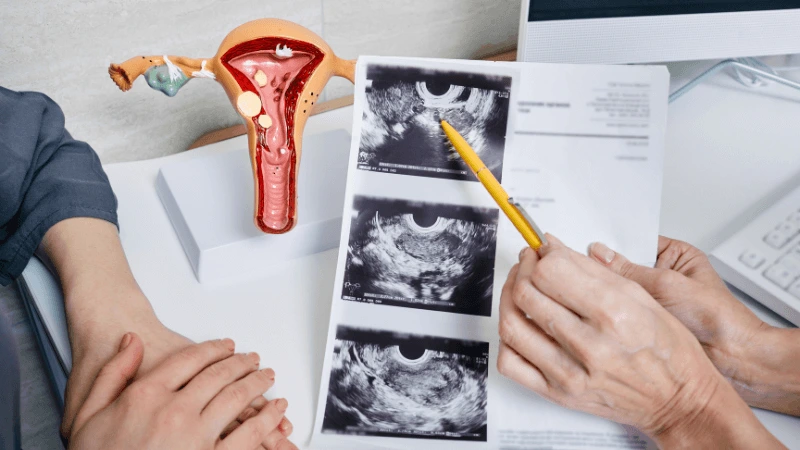
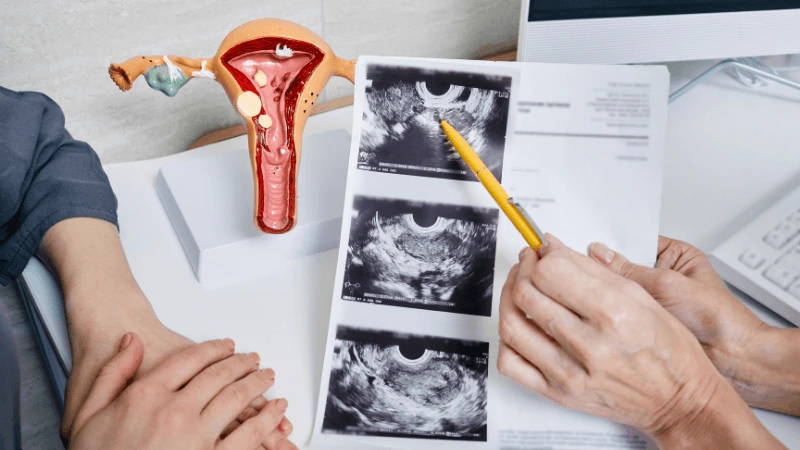
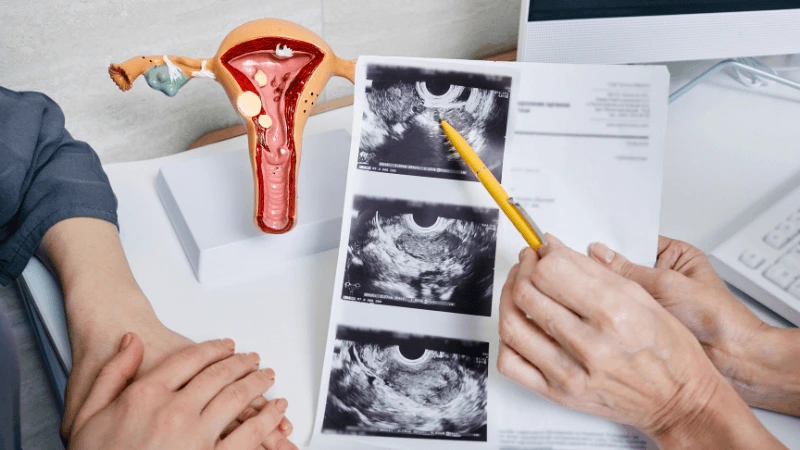
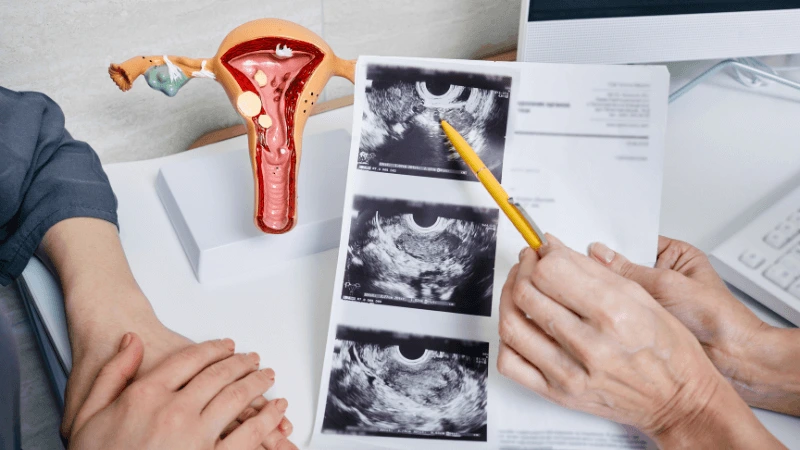
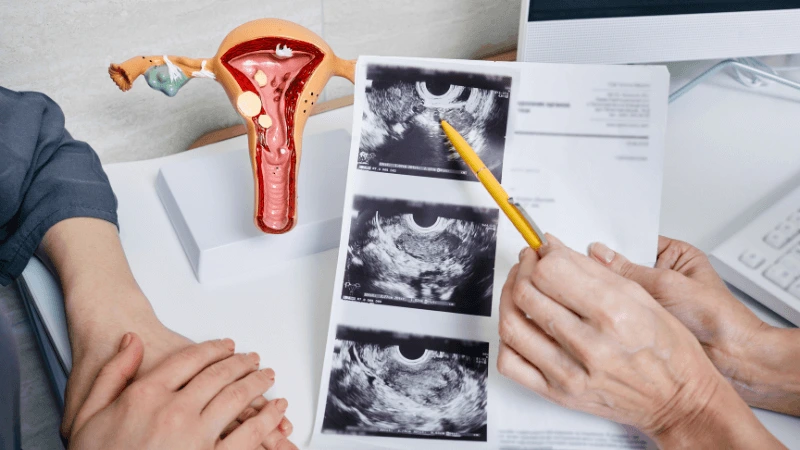
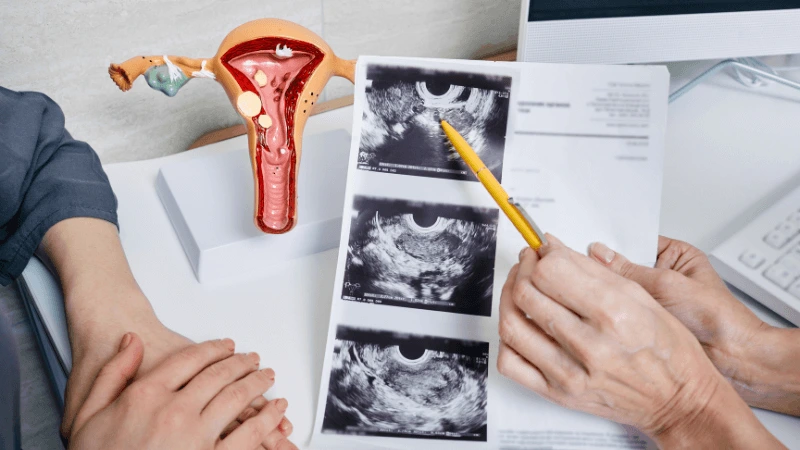
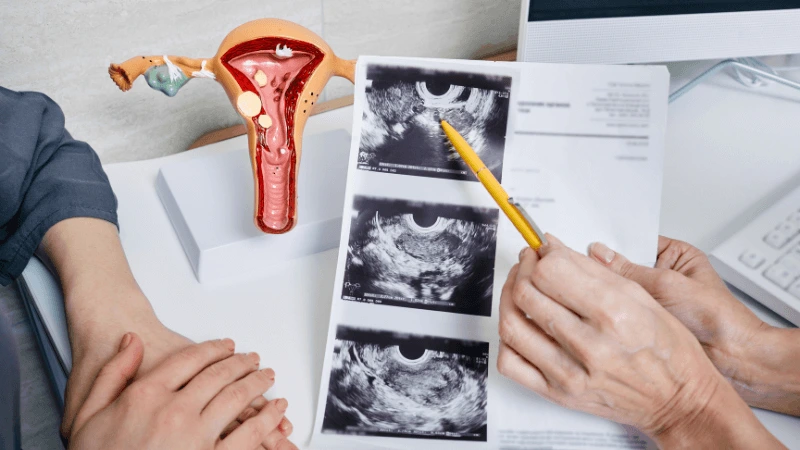
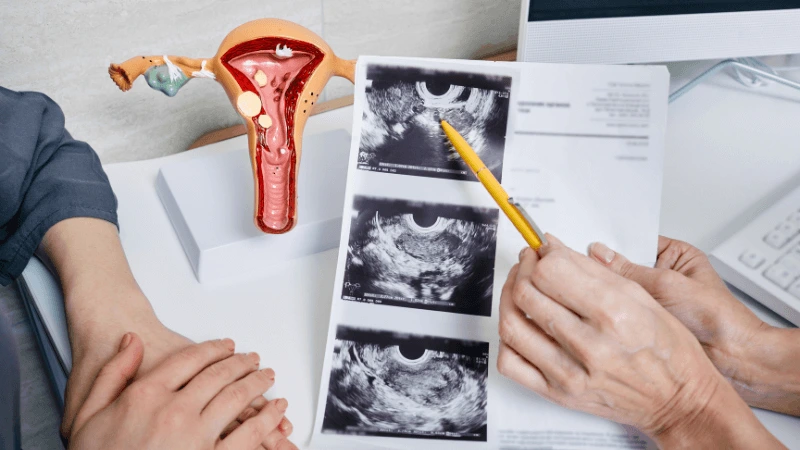
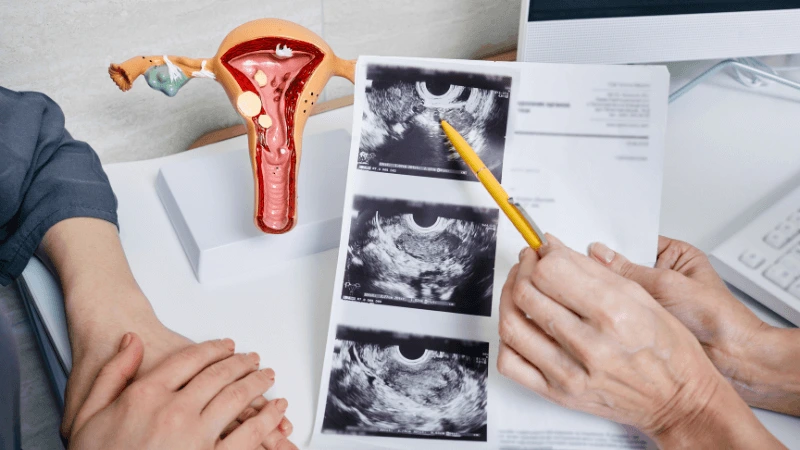
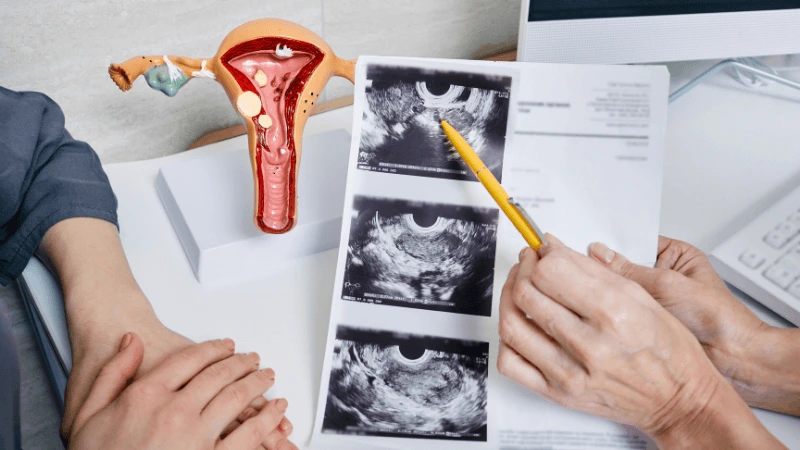
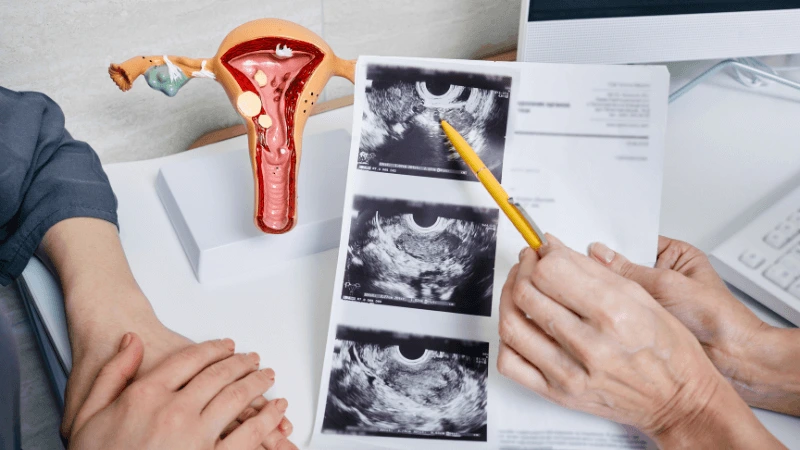
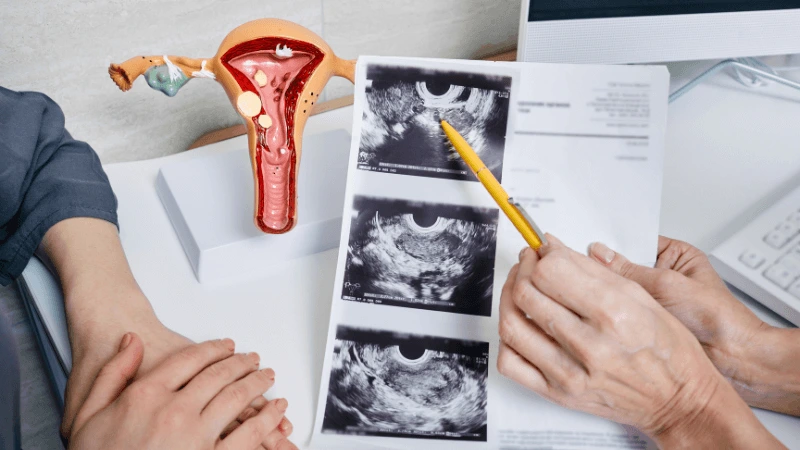
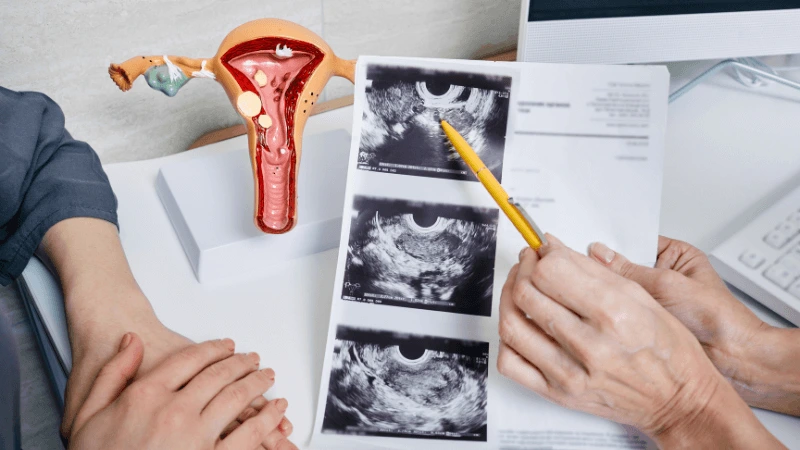
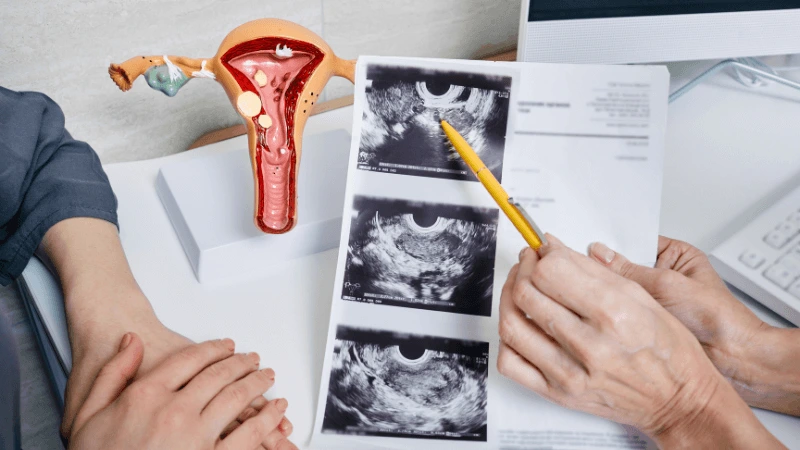
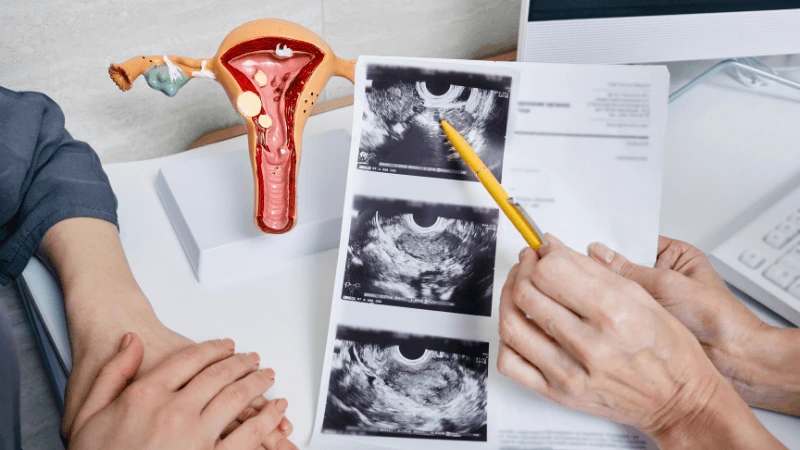
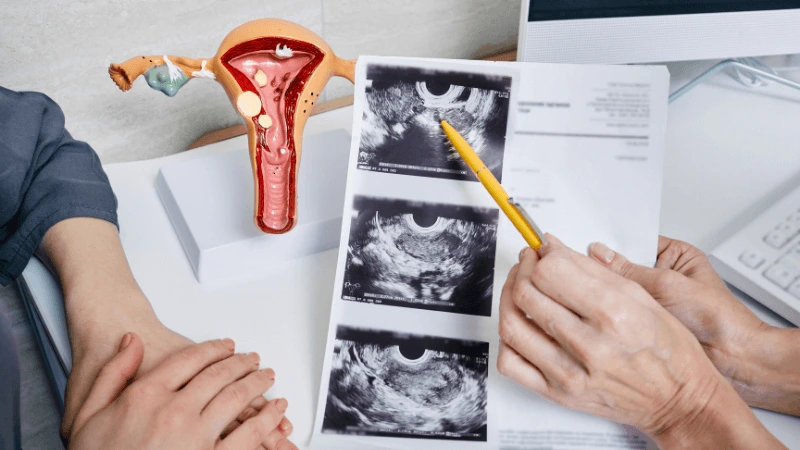
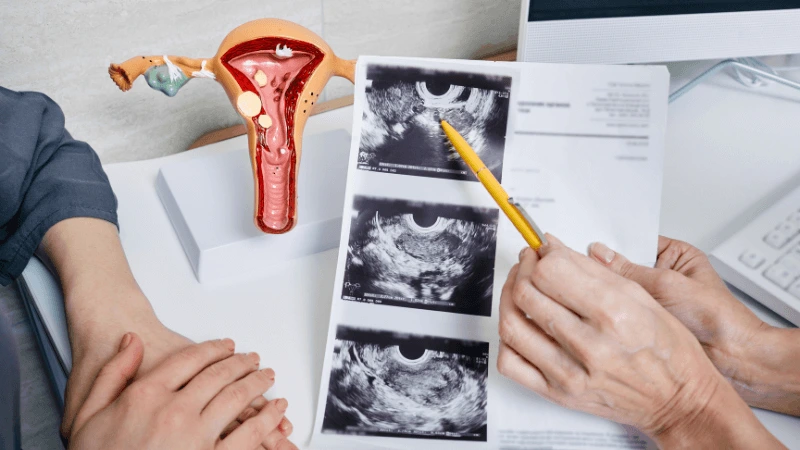
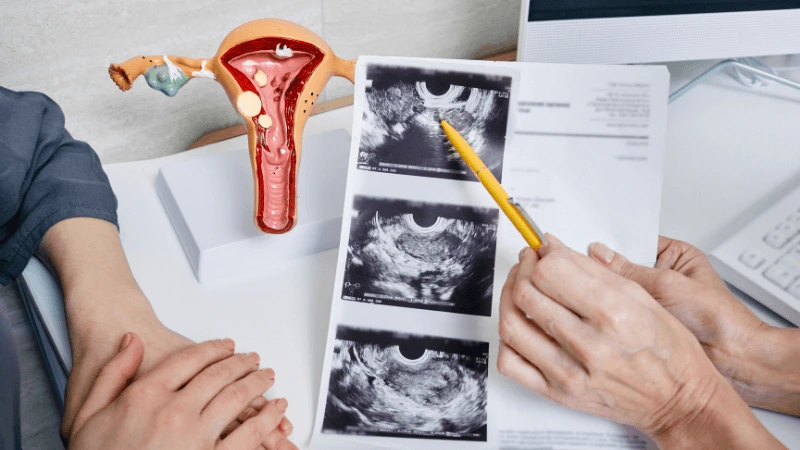
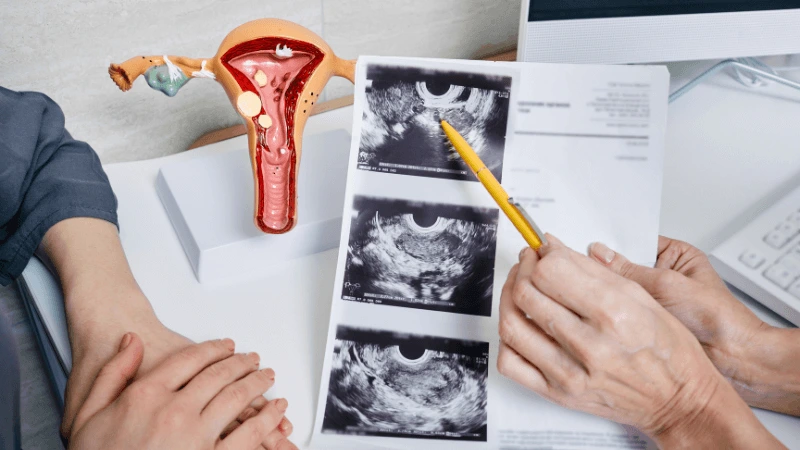
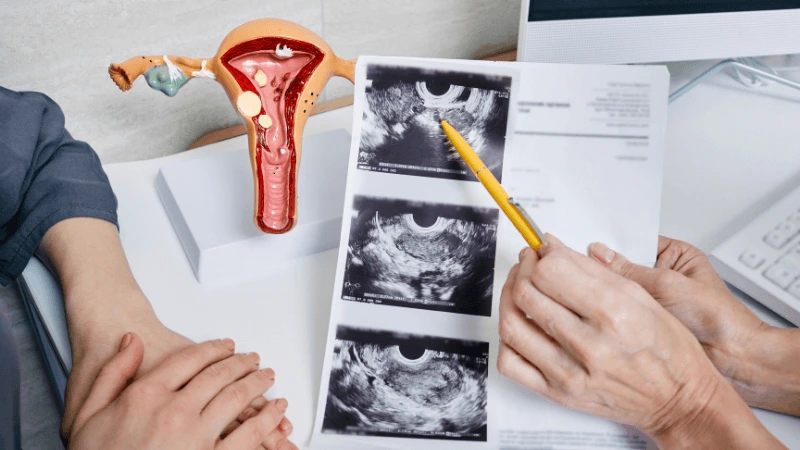
FALLOPIAN TUBE BLOCKAGE OPENING A fallopian tube blockage usually stops the egg from reaching the sperm or the fertilized egg from getting to the uterus. Surgery can help fix this common cause of infertility. The type of surgery depends on where and how severe the blockage is. Some tubal procedures can use microsurgical techniques. This can happen during open abdominal surgery or through laparoscopy using a small incision. The surgeon needs special training and skills in microsurgery and/or laparoscopy. This overview describes the most common tubal procedures. Tubal reanastomosis often reverses a tubal ligation or repairs a damaged part of the fallopian tube. The blocked or unhealthy part of the tube is removed, and the two healthy ends are joined. This usually requires an abdominal incision but some specialists can perform it using laparoscopy. Salpingectomy, or removal of part of a fallopian tube, improves in vitro fertilization (IVF) success when a tube has fluid build-up (hydrosalpinx). Hydrosalpinx makes IVF half as likely to succeed. Salpingectomy is preferred over salpingostomy for treating hydrosalpinx before IVF. Salpingostomy happens when the end of the fallopian tube is blocked by fluid build-up (hydrosalpinx). This creates a new opening in the part of the tube closest to the ovary. However, scar tissue often grows back after a salpingostomy, blocking the tube again. Fimbrioplasty may be recommended when the part of the tube near the ovary is partially blocked or has scar tissue, which prevents normal egg pickup. This rebuilds the fringed ends of the fallopian tube. For a blockage near the uterus, the first treatment option is a nonsurgical procedure called selective tubal cannulation. Using fluoroscopy or hysteroscopy for guidance, a doctor inserts a catheter, or cannula, through the cervix and uterus into the fallopian tube. What To Expect After Surgery After open abdominal surgery, expect a hospital stay of 2 to 3 days. Antibiotics may be given to prevent infection. A woman can typically return to work in 4 to 6 weeks, depending on the surgery extent, her job, and her overall health and energy level. After laparoscopic surgery, there is a short hospital stay. A woman may take a few days to a couple of weeks to get back to daily activities, based on the procedure type. Why It Is Done Fallopian tube surgery may be necessary if: - Hysterosalpingography shows blocked fallopian tubes. - A blocked fallopian tube has fluid build-up (hydrosalpinx). - You want to have a tubal ligation reversed.
Dr. Kapil Kanade is a highly trained Gynaec Laparoscopic & Infertility Specialist with extensive experience in treating fallopian tube blockages through minimally invasive procedures like hysteroscopic tubal cannulation and laparoscopic adhesiolysis.